
Take That, Internet Censors!
by Matt Taibbi | Jul 5. 2023
Here’s how federal judge Terry Doughty yesterday described the digital censorship controversy at which pundits a half-year now have repeatedly rolled eyes, dismissed, and mocked as a nothingburger: “If the allegations made by Plaintiffs are true, the present case arguably involves the most massive attack against free speech in United States’ history.”
Doughty then ordered a sweeping halt to the censorship schemes outlined in both the extant Missouri v. Biden lawsuit and in the Twitter Files. Critics who’ve been snickering about this issue might want to read this 155-page ruling now, and ask themselves if the current Supreme Court would or would not agree with Doughty. Still think this is a nothingburger?
With this ruling in the Missouri v. Biden censorship case, Doughty went out of his way on the Fourth of July, to issue a stern rebuke at a conga line of government officials, many of them characters in the Twitter Files. Racket readers will recognize names like Elvis Chan and Laura Dehmlow (of the FBI), Jen Easterly and Brian Scully (of the Department of Homeland Security), Laura Rosenberger (Special Assistant to the President, and one of the creators of Hamilton 68) and Daniel Kimmage (of the Global Engagement Center), who were all just ordered to get the hell off the First Amendment’s lawn. Paraphrasing, Doughty enjoined them from:
- meeting with social-media companies for the purpose of pressuring or inducing in any manner the removal or suppression of protected free speech;
- flagging posts on social-media platforms and/or forwarding to social-media companies urging the same;
- collaborating with the Election Integrity Partnership, the Virality Project, the Stanford Internet Observatory, or any “like project” or group for the same purpose;
- threatening or coercing social-media companies to remove protected free speech.
The New York Times, which instantly wrung its hands and stressed the ruling could “curtail efforts to fight disinformation,” grumblingly handed blame to the Twitter Files, without naming them of course, and mislabeling it as a partisan enterprise:
Elon Musk has echoed Republican arguments, releasing internal company documents to chosen journalists suggesting what they claimed was collusion between company and government officials. Though that remains far from proven, some of the documents Mr. Musk disclosed ended up in the lawsuit’s arguments.
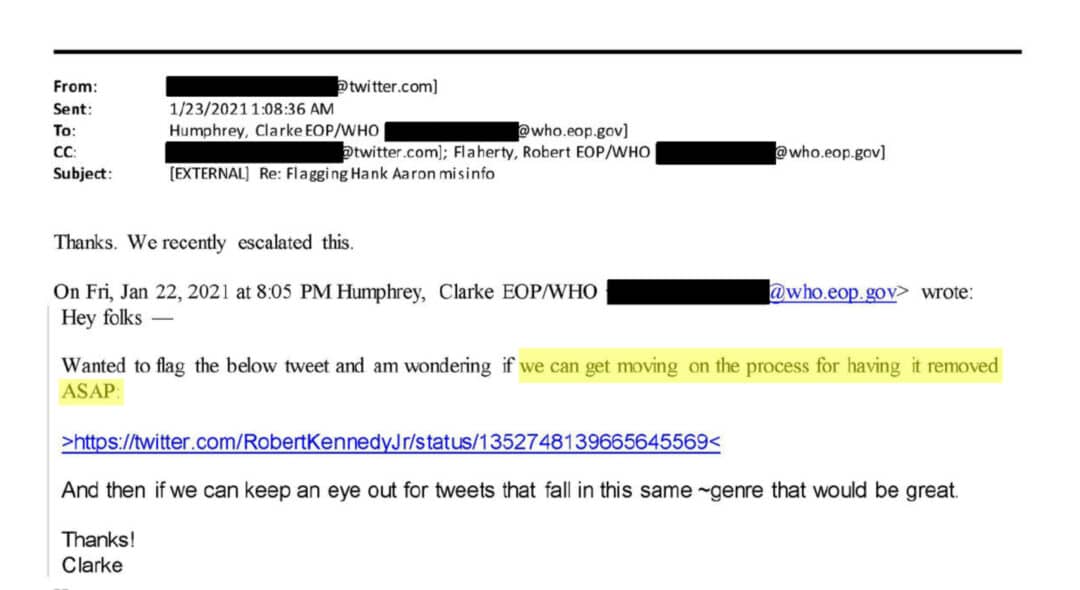
The investigation led by Louisiana Attorney General Jeff Landry and Missouri’s Andrew Bailey, produced documents showing overt government requests to censor people like Robert F. Kennedy, Jr., a White House official expressing frustration to Facebook that they weren’t “removing bad information from search,” and emails in which a Facebook official pleads with the White House to understand that they’re already “reducing the virality” of “often-true content” that might promote vaccine hesitancy, among many other things. The Attorneys General likewise scored depositions with people like Dr. Anthony Fauci, and confronted him with documents showing Facebook sending his office updates about how “we are expanding the list of false claims we will remove.”
Was this illegal? Unconsititional? Did it show a pattern of mighty tech companies like Facebook and Twitter acting like they were reporting to federal officials like Fauci on content moderation? I knew what I thought it looked like, but what judges or a jury might say, who knew?
Yesterday’s ruling, which naturally will be dismissed as Republican clickbait, shows at least one federal judge agreed with the argument that a complex system to mass-funnel content recommendations from enforcement agencies and politicians to tech platforms represents what the Attorneys General called a “sprawling federal ‘Censorship Enterprise.’” As one of the plaintiffs, Dr. Aaron Kheriaty wrote, the evidence in the suit revealed a far broader range of topics monitored by government than most people know of even now, from gender ideology to abortion to monetary policy to the war in Ukraine and beyond.
“Take any contentious issue in American public life,” said Kheriaty today, “and it seems like the federal government, once they got this machinery rolling, just thought, ‘Okay, we can combat quote-unquote misinformation on all kinds of things.’”
The Missouri v. Biden investigators found the same fact patterns found by Twitter Files reporters like me, Michael Shellenberger, Bari Weiss, Lee Fang, David Zweig, and Paul Thacker, and then later Andrew Lowenthal, Aaron Mate, Sue Schmidt, Matt Orfalea, Tom Wyatt, Matt Farwell, @Techno_Fog, and many others did. They also echoed descriptions by like Jacob Siegel at Tablet, or Robby Soave at Reason, who wrote about similar issues at Facebook.
Those of us who worked on the Twitter Files story initially experienced the same problem investigators and plaintiffs in the Missouri v. Biden case apparently did, being unsure of what to make of the sheer quantity of agencies and companies involved in what looked like organized censorship schemes. I know I wasn’t alone among Twitter Files reporters in being nervous to report that content moderation “requests” were coming from “agencies across the federal government — from the State Department to the Pentagon to the CIA.” It’s what we were seeing, but seemed too nuts to be true. But as time went on, even more topics, government offices, and state-partnered organizations started popping up, leaving little question of what we were looking at.
Eventually, we found the same plot outlined in Missouri v. Biden: pressure from government in the form of threatened regulation, followed by a stream of recommendations about content from multiple agencies (the investigators in this lawsuit even found meddling by the Census Bureau). This was capped by the construction of quasi-private bureaucracies that in some cases appeared to have been conceived as a way for the government to partner on content moderation without being in direct violation of the First Amendment.
Most of us covering the Twitter Files tried to avoid delving into the constitutionality/legality question, but couldn’t help wondering in some cases, for instance with Stanford’s Election Integrity Partnership and Virality Partnership, which created cross-platform content ticketing systems about the 2020 race and Covid-19. We all thought we were looking at a potentially major problem there, since the principals from places like Stanford weren’t shy about saying they wanted to “fill the gap of the things that the government cannot do themselves” because partners like DHS/CISA lacked “the funding and the legal authorizations” to do the work.
What might happen if judges or juries were presented with that whole picture, including details about the open, ongoing partnerships of these groups with government agencies like CISA and the Surgeon General? We have some idea now.
The dismissal of these complaints as partisan “tinfoil hat” conspiracy by politicians like the ones who interrogated Michael Shellenberger and me in Congress, and by papers like the New York Times and Washington Post, has all along felt like the the same kind of error that led to the mis-call of the 2016 election and the massive loss of audience for traditional media stations in the years that ensued.
These mainstream news observers are trapped in a bubble of their own making and can’t or won’t see that the average American looks at letters from the White House to shut down social media accounts, or piles of “suggestions” on content from the FBI, and feels instinctively that he or she really doesn’t like that, whatever it is. One can hope at least a few censorship advocates will read the ruling and grasp that in a democracy, you can’t have a situation where only half (or less) of the population thinks something as basic as the speech landscape is fairly arranged. That just won’t hold, making rulings like this foreseeable, if not inevitable. No matter what, this can’t be anything but good news for the First Amendment.
“Hopefully,” said Kheriaty, “yesterday was the beginning of the end of the censorship Leviathan.”





0 Comments